Publications
2025

Yigit, Nevzat; Föttinger, Karin; Bernardi, Johannes; Rupprechter, Günther
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: Journal of Catalysis, iss. 0021-9517, pp. 115973, 2025.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P08, P10
@article{Yigit_2024a,
title = {Preferential CO oxidation (PROX) on LaCoO_{3}–based catalysts: Effect of cobalt oxidation state on selectivity},
author = {Nevzat Yigit and Karin Föttinger and Johannes Bernardi and Günther Rupprechter},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2025.115973},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-20},
urldate = {2025-01-20},
journal = {Journal of Catalysis},
issue = {0021-9517},
pages = {115973},
abstract = {The perovskite LaCoO_{3} (LCO) was used as catalyst for preferential oxidation of CO (PROX). LCO was synthesized via the modified Pechini method and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and CO_{2–} and H_{2–} temperature programmed reduction (TPR). Different reductive and oxidative pretreatments were applied to systematically vary the Co oxidation state in order to examine its effect on catalytic performance and to single out active site requirements. Upon reduction at increasing temperature, LaCoO_{3} transformed to brownmillerite-type La_{2}Co_{2}O_{5}, exsolved Co^{0} nanoparticles supported on La_{2}O_{3} and, upon reoxidation, to Co_{3}O_{4}/La_{2}O_{3}. The Co oxidation state of the various catalysts correlated with their CO_{2} selectivity: LCO containing only Co^{3+} exhibited 100 % CO_{2} selectivity in a wide temperature window, whereas La_{2}Co_{2}O_{5}, Co/La_{2}O_{3} and Co_{3}O_{4}/La_{2}O_{3} had markedly lower selectivity. It is suggested that Co^{3+} is crucial and that the strong resistivity of LaCoO_{3} towards reduction is responsible for the high and stable CO_{2} selectivity over a temperature range of 100 °C–220 °C. Higher oxygen concentration further broadens the PROX window.},
keywords = {P08, P10},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024
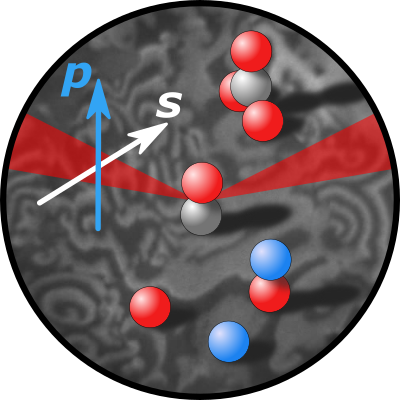
Li, Xia; Rupprechter, Günther
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: Surface Science Reports, vol. 79, iss. 4, pp. 100645, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P08
@article{Li_2024a,
title = {Sum frequency generation (SFG) spectroscopy at surfaces and interfaces: Adsorbate structure and molecular bond orientation},
author = {Xia Li and Günther Rupprechter},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2024.100645},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-12-05},
urldate = {2024-12-05},
journal = {Surface Science Reports},
volume = {79},
issue = {4},
pages = {100645},
abstract = {Infrared (IR)-visible (Vis) sum frequency generation (SFG) is a second-order nonlinear optical process which is forbidden in centrosymmetric bulk media or isotropic phases, but allowed at (open) surfaces or (buried) interfaces where the inversion symmetry is broken. SFG spectroscopy is thus inherently surface- or interface-specific, providing information about the structure, orientation, surface number density, chirality, and dynamics of molecules, provided the system of interest is accessible by light. This review illustrates basic SFG concepts, theory, operation modes (e.g., frequency-domain, broadband, homodyne/heterodyne, time-resolved), and recent extensions and developments of SFG (e.g., doubly resonant, plasmon-enhanced, chiral, microscopy). To illustrate the wide range of SFG applications, selected case studies discuss the characterization of molecular structure and bond orientation at solid-gas, solid-liquid, liquid-air, liquid-liquid, and solid-solid interfaces.},
keywords = {P08},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
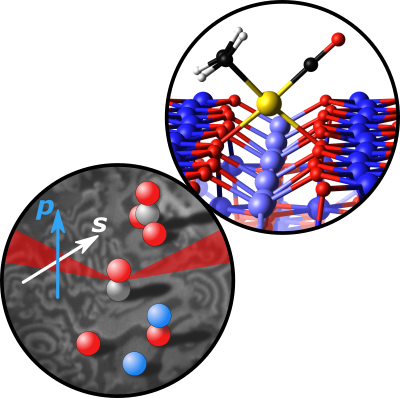
Tangpakonsab, Parinya; Genest, Alexander; Parkinson, Gareth S.; Rupprechter, Günther
Journal ArticleOpen AccessSubmittedIn: ChemRxiv, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P04, P08
@article{Tangpakonsab_2024a,
title = {Mechanistic Insights into CO and H_{2} Oxidation on Cu/CeO_{2} Single Atom Catalysts: A Computational Investigation},
author = {Parinya Tangpakonsab and Alexander Genest and Gareth S. Parkinson and Günther Rupprechter},
url = {https://chemrxiv.org/engage/chemrxiv/article-details/673325d25a82cea2fadefd76},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-11-14},
urldate = {2024-11-14},
journal = {ChemRxiv},
abstract = {Single atom catalysts (SACs) have attracted significant interest due to their unique properties and potential for enhancing catalytic performance in various chemical reactions. In this study, we atomistically explore adsorption properties and catalytic performance of single Cu atoms anchored at low-index CeO_{2} surfaces, focusing on the oxidation of CO and H_{2}. Utilizing density functional theory (DFT) calculations, we report that Cu adatoms bind favorably on different CeO_{2} surfaces, following a stability order of (100)>(110)>(111). The charge transfer from a single adsorbed Cu atom to Ce leads to the reduction of Ce^{4+} to Ce^{3+} and the oxidation of Cu^{0} to Cu^{+}. This strengthens molecular bonds at Cu sites, particularly for CO due to the less populated d-band, while H_{2} shows a by ~1 eV weaker adsorption. CO oxidation is energetically more favorable than H_{2} oxidation on the Cu/CeO_{2}(111) surface. The rate-controlling steps for the Mars-van Krevelen oxidation involve the formation of a bent CO_{2}^{-} intermediate for CO and H_{2}O for H_{2}. The lattice oxygen atom at the interface plays a key role for both oxidation processes. Our findings highlight the potential of single atom catalyst, Cu/CeO_{2}, for CO adsorption and oxidation in heterogeneous catalysis.},
keywords = {P04, P08},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
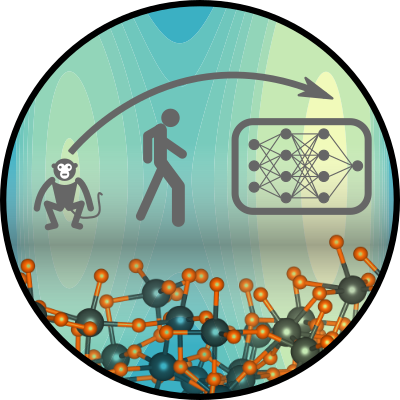
Bichelmaier, Sebastian; Carrete, Jesús; Madsen, Georg K. H.
Neural network enabled molecular dynamics study of HfO2 phase transitions
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: Phys. Rev. B, vol. 110, pp. 174105, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P09
@article{Bichelmaier_2024a,
title = {Neural network enabled molecular dynamics study of HfO_{2} phase transitions},
author = {Sebastian Bichelmaier and Jesús Carrete and Georg K. H. Madsen},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.02429},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.110.174105},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-11-07},
journal = {Phys. Rev. B},
volume = {110},
pages = {174105},
abstract = {The advances of machine-learned force fields have opened up molecular dynamics (MD) simulations for compounds for which ab initio MD is too resource intensive and phenomena for which classical force fields are insufficient. Here we describe a neural-network force field parametrized to reproduce the r2SCAN potential energy landscape of HfO_{2}. Based on an automatic differentiable implementation of the isothermal-isobaric (𝑁𝑃𝑇) ensemble with flexible cell fluctuations, we study the phase space of HfO_{2}. We find excellent predictive capabilities regarding the lattice constants and experimental x-ray diffraction data. The phase transition away from monoclinic is clearly visible at a temperature around 2000 K, in agreement with available experimental data and previous calculations. Another abrupt change in lattice constants occurs around 3000 K. While the resulting lattice constants are closer to cubic, they exhibit a small tetragonal distortion, and there is no associated change in volume. We show that this high-temperature structure is in agreement with the available high-temperature diffraction data.},
keywords = {P09},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Redondo, Jesus; Reticcioli, Michele; Gabriel, Vit; Wrana, Dominik; Ellinger, Florian; Riva, Michele; Franceschi, Giada; Rheinfrank, Erik; Sokolovic, Igor; Jakub, Zdenek; Kraushofer, Florian; Alexander, Aji; Patera, Laerte L.; Repp, Jascha; Schmid, Michael; Diebold, Ulrike; Parkinson, Gareth S.; Franchini, Cesare; Kocan, Pavel; Setvin, Martin
Real-space investigation of polarons in hematite Fe2O3
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: Science Advances, vol. 10, iss. 44, pp. eadp7833, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P02, P04, P07
@article{Redondo2024,
title = {Real-space investigation of polarons in hematite Fe_{2}O_{3}},
author = {Jesus Redondo and Michele Reticcioli and Vit Gabriel and Dominik Wrana and Florian Ellinger and Michele Riva and Giada Franceschi and Erik Rheinfrank and Igor Sokolovic and Zdenek Jakub and Florian Kraushofer and Aji Alexander and Laerte L. Patera and Jascha Repp and Michael Schmid and Ulrike Diebold and Gareth S. Parkinson and Cesare Franchini and Pavel Kocan and Martin Setvin},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.17945
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adp7833},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-11-01},
urldate = {2024-09-27},
journal = {Science Advances},
volume = {10},
issue = {44},
pages = {eadp7833},
abstract = {In polarizable materials, electronic charge carriers interact with the surrounding ions, leading to quasiparticle behaviour. The resulting polarons play a central role in many materials properties including electrical transport, optical properties, surface reactivity and magnetoresistance, and polaron properties are typically investigated indirectly through such macroscopic characteristics. Here, noncontact atomic force microscopy (nc-AFM) is used to directly image polarons in Fe_{2}O_{3} at the single quasiparticle limit. A combination of Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) and kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) simulations shows that Ti doping dramatically enhances the mobility of electron polarons, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations indicate that a metallic transition state is responsible for the enhancement. In contrast, hole polarons are significantly less mobile and their hopping is hampered further by the introduction of trapping centres.},
keywords = {P02, P04, P07},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Romano, Salvatore; Kaur, Harsharan; Zelenka, Moritz; Hijes, Pablo Montero De; Eder, Moritz; Parkinson, Gareth S.; Backus, Ellen H. G.; Dellago, Christoph
Journal ArticleOpen AccessSubmittedarXivIn: arXiv, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P04, P11, P12
@article{Romano_2024b,
title = {Structure of the water/magnetite interface from sum frequency generation experiments and neural network based molecular dynamics simulations},
author = {Salvatore Romano and Harsharan Kaur and Moritz Zelenka and Pablo Montero De Hijes and Moritz Eder and Gareth S. Parkinson and Ellen H. G. Backus and Christoph Dellago},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.12717},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-16},
urldate = {2024-10-16},
journal = {arXiv},
abstract = {Magnetite, a naturally abundant mineral, frequently interacts with water in both natural settings and various technical applications, making the study of its surface chemistry highly relevant. In this work, we investigate the hydrogen bonding dynamics and the presence of hydroxyl species at the magnetite-water interface using a combination of neural network potential-based molecular dynamics simulations and sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy. Our simulations, which involved large water systems, allowed us to identify distinct interfacial species, such as dissociated hydrogen and hydroxide ions formed by water dissociation. Notably, water molecules near the interface exhibited a preference for dipole orientation towards the surface, with bulk-like water behavior only re-emerging beyond 60 Å from the surface. The vibrational spectroscopy results aligned well with the simulations, confirming the presence of a hydrogen bond network in the surface ad-layers. The analysis revealed that surface-adsorbed hydroxyl groups orient their hydrogen atoms towards the water bulk. In contrast, hydrogen-bonded water molecules align with their hydrogen atoms pointing towards the magnetite surface.},
keywords = {P04, P11, P12},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Rakngam, Issaraporn; Alves, Gustavo A. S.; Osakoo, Nattawut; Wittayakun, Jatuporn; Konegger, Thomas; Föttinger, Karin
Journal ArticleOpen AccessAccepted ArticleIn: RSC Sustainability, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P10
@article{Rakngama_2024a,
title = {Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnZrO_{x} catalysts for CO_{2} hydrogenation to methanol: the effect of pH on structure and activity},
author = {Issaraporn Rakngam and Gustavo A. S. Alves and Nattawut Osakoo and Jatuporn Wittayakun and Thomas Konegger and Karin Föttinger},
doi = {10.1039/D4SU00522H},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-11},
urldate = {2024-10-11},
journal = {RSC Sustainability},
abstract = {With the growing necessity of achieving carbon neutrality in the industrial sector, the catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide into methanol has been widely considered one of the key strategies for the utilization of captured CO_{2}. For this reason, the development of alternative catalysts such as ZnZrO_{x} has attracted considerable interest, given its superior stability and versatility in comparison to the conventional Cu-based materials. In this work, ZnZrO_{x} has been produced by a hydrothermal synthesis method at varied synthesis pH between 7 and 10 and a positive association between pH and catalytic CO_{2} conversion is observed. At 2.0 MPa and 250 °C, ZnZrO_{x} produced at pH 10 shows a methanol selectivity of 95% at a CO_{2} conversion of 3.4%. According to characterization, basic pH conditions enable the formation of abundant t-ZrO_{2} and the subsequent incorporation of Zn^{2+} into this phase, although the content of surface Zn does not increase between pH 8 and 10. Nevertheless, synthesis pH values can be correlated with surface oxygen content and CO_{2} adsorption capacity, which could be important contributors to the higher catalytic activity observed as a result of higher synthesis pH values. Finally, the comparison between NaOH and NH_{4}OH as additives to adjust pH 10 indicate similar catalytic activities and surface properties, which emphasizes the proposed trend between hydrothermal synthesis pH and catalytic activity for CO_{2} hydrogenation.},
keywords = {P10},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Schrenk, Florian; Lindenthal, Lorenz; Drexler, Hedda; Berger, Tobias; Rameshan, Raffael; Ruh, Thomas; Föttinger, Karin; Rameshan, Christoph
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: RSC Sustainability, vol. 2, iss. 11, pp. 3334-3344, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P10
@article{Schrenk_2024a,
title = { How reduction temperature influences the structure of perovskite-oxide catalysts during the dry reforming of methane},
author = {Florian Schrenk and Lorenz Lindenthal and Hedda Drexler and Tobias Berger and Raffael Rameshan and Thomas Ruh and Karin Föttinger and Christoph Rameshan},
doi = {10.1039/d4su00483c},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-04},
urldate = {2024-10-04},
journal = {RSC Sustainability},
volume = {2},
issue = {11},
pages = {3334-3344},
abstract = {Dry reforming of methane is a promising reaction to convert CO_{2} and combat climate change. However, the reaction is still not feasible in large-scale industrial applications. The thermodynamic need for high temperatures and the potential of carbon deposition leads to high requirements for potential catalyst materials. As shown in previous publications, the Ni-doped perovskite-oxide Nd_{0.6}Ca_{0.4}Fe_{0.97}Ni_{0.03}O_{3} is a potential candidate as it can exsolve highly active Ni nanoparticles on its surface. This study focused on controlling the particle size by varying the reduction temperature. We found the optimal temperature that allows the Ni nanoparticles to exsolve while not yet enabling the formation of deactivating CaCO_{3}. Furthermore, the exsolution process and the behaviour of the phases during the dry reforming of methane were investigated using in-situ XRD measurements at the DESY beamline P02.1 at PETRA III in Hamburg. They revealed that the formed deactivated phases would, at high temperatures, form a brownmillerite phase, thus hinting at a potential self-healing mechanism of these materials. },
keywords = {P10},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
de Hijes, Pablo Montero; Dellago, Christoph; Jinnouchi, Ryosuke; Kresse, Georg
Density isobar of water and melting temperature of ice: Assessing common density functionals
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: The Journal of Chemical Physics, vol. 161, pp. 131102, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: P03, P12
@article{Montero-de-Hijes_2024b,
title = {Density isobar of water and melting temperature of ice: Assessing common density functionals},
author = {Pablo Montero de Hijes and Christoph Dellago and Ryosuke Jinnouchi and Georg Kresse},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0227514},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-03},
urldate = {2024-06-06},
journal = {The Journal of Chemical Physics},
volume = {161},
pages = {131102},
abstract = {We investigate the density isobar of water and the melting temperature of ice using six different density functionals. Machine-learning potentials are employed to ensure computational affordability. Our findings reveal significant discrepancies between various base functionals. Notably, even the choice of damping can result in substantial differences. Overall, the outcomes obtained through density functional theory are not entirely satisfactory across most utilized functionals. All functionals exhibit significant deviations either in the melting temperature or equilibrium volume, with most of them even predicting an incorrect volume difference between ice and water. Our heuristic analysis indicates that a hybrid functional with 25% exact exchange and van der Waals damping averaged between zero and Becke–Johnson dampings yields the closest agreement with experimental data. This study underscores the necessity for further enhancements in the treatment of van der Waals interactions and, more broadly, density functional theory to enable accurate quantitative predictions for molecular liquids.},
keywords = {P03, P12},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Li, Xia; Rupprechter, Günther
Journal ArticleOpen AccessIn: Surface Science Reports, no. 100645, 2024, ISSN: 0167-5729.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags:
@article{Li2024,
title = {Sum frequency generation (SFG) spectroscopy at surfaces and interfaces: Adsorbate structure and molecular bond orientation},
author = {Xia Li and Günther Rupprechter},
doi = {10.1016/j.surfrep.2024.100645},
issn = {0167-5729},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-01},
urldate = {2024-10-01},
journal = {Surface Science Reports},
number = {100645},
publisher = {Elsevier BV},
abstract = {Infrared (IR)-visible (Vis) sum frequency generation (SFG) is a second-order nonlinear optical process which is forbidden in centrosymmetric bulk media or isotropic phases, but allowed at (open) surfaces or (buried) interfaces where the inversion symmetry is broken. SFG spectroscopy is thus inherently surface- or interface-specific, providing information about the structure, orientation, surface number density, chirality, and dynamics of molecules, provided the system of interest is accessible by light. This review illustrates basic SFG concepts, theory, operation modes (e.g., frequency-domain, broadband, homodyne/heterodyne, time-resolved), and recent extensions and developments of SFG (e.g., doubly resonant, plasmon-enhanced, chiral, microscopy). To illustrate the wide range of SFG applications, selected case studies discuss the characterization of molecular structure and bond orientation at solid-gas (air, UHV), solid-liquid, liquid-air, liquid-liquid, and solid-solid interfaces.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}